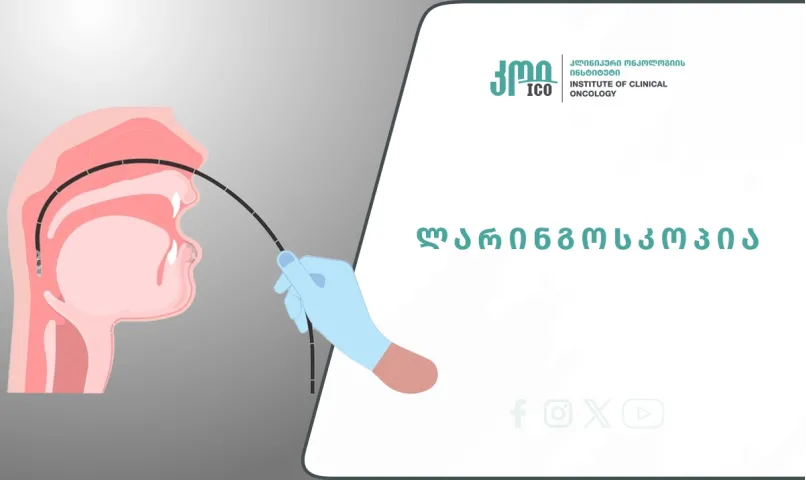
Laringoscopy is an endoscopic examination used for a detailed assessment of the larynx and upper respiratory tract. The procedure is performed using a special flexible video endoscope, which offers several significant advantages over standard methods. In particular, the endoscope enables visual examination not only of the larynx but also of the oropharynx, nasopharynx, and nasal tissues.
When is a laryngoscopy indicated?
This examination is recommended in the following cases:
- Chronic or unexplained sore throat;
- Causeless earache;
- Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing);
- A foreign body sensation in the throat;
- Damage to the larynx;
- Airway obstruction.
Also, this method of diagnosis is especially important in the case of:
- Change in voice timbre;
- Hoarseness or harshness of voice;
- Harsh sound;
- Partial or complete loss of voice;
- Bloody nose.
Benefits of Laringoscopy
- This is an informative and reliable diagnostic method;
- Video recording is possible during the procedure;
- A precise diagnosis can be made in just 5 minutes;
- The method is safe and minimally traumatizing;
- Possibility of minimal invasions, such as taking a biopsy or removing polyps.
Side effects and possible complications of laryngoscopy
The risk of complications is minimal for all types of laryngoscopy, although it increases if the patient has acute respiratory failure.
Preparation for the procedure
It is recommended to cease eating and drinking 8 hours before laryngoscopy to prevent vomiting.
Procedure for performing a laryngoscopy
The examination is performed using a flexible video endoscope - a laryngoscope. During the procedure, the doctor can:
- Take a biopsy;
- Remove polyps endoscopically.
After the procedure finishes, the patient gets video material, and the removed sample is sent for histological or cytological analyses. As a rule, the test result is ready within a 7-10 working day period.
Laryngoscopy is a modern, fast, and effective method for diagnosing and managing vocal, throat, and airway problems.
- Views:6414